Conversation with dysfunctional families in the dow. Algorithm for identifying, preventing and eliminating family problems
Topic: Prevention of family troubles
Vyshny Volochek 2012


Prevention of family trouble
is the process of taking action to prevent the family from losing the opportunity to meet their needs

The purpose of our today's lesson is: to learn how to identify children who need specialist help, and to understand what kind of help a child needs.
The tasks that we must solve to achieve the goal are the following:
1. Determine the criteria for family dysfunction (i.e. which families can and should be considered dysfunctional)
2. Consider the system of services and officials for working with such families
3. Learn to identify dysfunctional families
4. Offer possible options for helping a dysfunctional family.

antisocial behavior
antisocial behavior
Inappropriate Parental Responsibilities
Violence in family


Forms of identifying dysfunctional families:
Providing material assistance;
Influence through the media;
Creation of interest clubs;
Permanent patronage;
Treatment for alcoholism;
administrative fines;
Deprivation of parental rights;

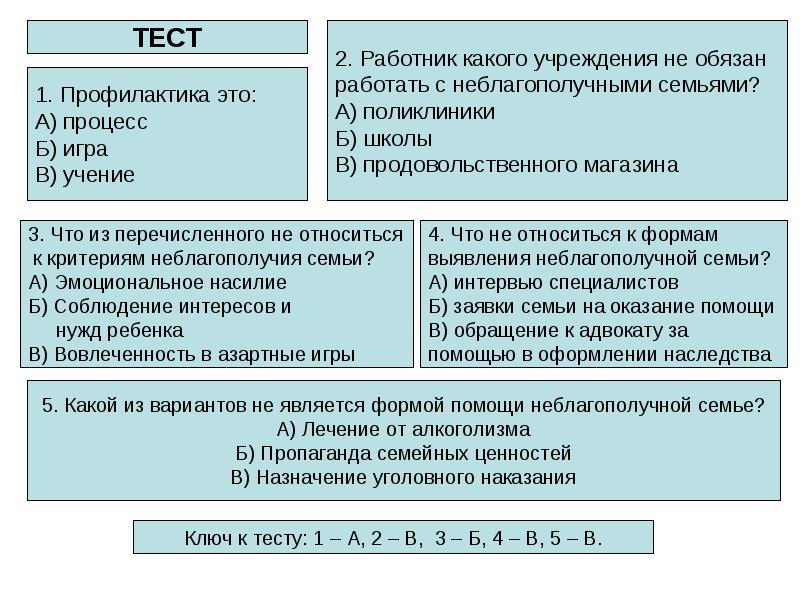
Test
Test
"Family Drawing"


Help for a disadvantaged family:
Treatment for alcoholism;
Deprivation of parental rights;
Consulting; Educational consultations for parents;
Assistance of public organizations;
Influence through the media;
Promotion of healthy lifestyles;
Promotion of family values;
Providing material assistance;
administrative fines;
Creation of interest clubs;
Permanent patronage;
Providing free meals to children from disadvantaged families;
Free treatment of children and rehabilitation during the holidays;
Interaction of all services in early detection and individual approach to solving the problems of each family.

1. What is the topic of the lesson?
1. What is the topic of the lesson?
2. What is prevention?
3. What can you say about family problems?
4. What are the criteria for family trouble?
5. What methodology did we use today to identify a dysfunctional family?

Task
Questions for the task:
1. Can this family be called dysfunctional and why?
2. How can the disadvantaged family be identified and who can do it?
3. What kind of help and what specialists does this family need?
A boy named Ivan, 8 years old, lives with his mother and grandmother in a private house, consisting of 3 rooms. Grandmother is a pensioner, mother (25 years old) often does not sleep or comes home late, does not work. Ivan often misses classes at school, has no friends, spends his free time at home. By nature, he is quick-tempered, the psyche is unbalanced, he can freely be rude to elders and teachers at school. Mother loves Ivan, often buys toys for him.

Homework:
Homework:
1. Learn lecture material
2. Analyze the picture of your family, drawn by you today in the lesson.
Literature and Internet sources:
1. Alekseeva L.S. Technologies of social work with children affected by domestic violence: Scientific and methodological manual. - M, 2001.
2. Ovcharova R.V. Reference book of the social pedagogue. - M .: TC Sphere, 2005.
3. Kholostova E.I. Social work with the family: Textbook / E.I. Kholostov. - 3rd edition - M .: Ed. "Dashkov and K0", 2009.
4. Eidemiller. E.G. Methods of family diagnostics and psychotherapy. - M., 1996
5. http://oganyanaa.narod2.ru
Thanks for the lesson

“Children are our old age. Proper upbringing is our happy old age, bad upbringing is future grief, these are our tears, this is our fault before other people, before the whole country.
A. S. Makarenko
Rationale for the relevance of the article
Our village is located ten kilometers from the city of Nazarovo - this is both good and bad. Our once prosperous village suddenly turned into an economically unstable one. The poultry farm five years ago was an exemplary farm not only in the region, but also in Russia. Now this enterprise turned out to be unprofitable and unpromising.
There were very rich and very poor. Both have the same conditions for housekeeping, but most have already developed social pessimism.
This is one of the reasons for the social instability of the village, the decline in moral principles in the family, among the youth and adolescents.
In the last two years alone, the number of low-income families has almost doubled in our country, and there are more dysfunctional families. The psychological climate is also deteriorating in stable families. home reason is absence livelihood, the threat of unemployment, malnutrition, rising prices for food, services. A sharp increase in stressful situations affects children. Lack of care in families, psychological deprivation, physical and sexual abuse pushes children to run away. It is family trouble that is a prerequisite for various deformations of the process of socialization of the child's personality, which ultimately manifests itself in neglect or homelessness of minors. Most of those who work with children have come to the conclusion that it is easier to do everything possible so that the child does not end up “on the street” than to return him “off the street” to normal life.
Based on observations, testing, questioning, an algorithm was developed to identify, prevent and eliminate family troubles.
1. COLLABORATE:
- Organs social protection population
- Education department;
- Internal affairs bodies;
- Health;
- Department for youth policy;
- Public Employment Service;
- rural administration;
- RKDN.
2. SOURCES OF INFORMATION ABOUT FAMILY DISCOMFORT:
- class teachers;
- Kindergarten teachers;
- school teachers;
- Doctors;
- district inspector;
- Villagers;
- Relatives;
- Neighbours;
- Friends.
3. AN ADDITIONAL SOURCE IS:
- Documents of social and medical patronage;
- Documents of the psychological and pedagogical council at the school;
- Materials of psychodiagnostics;
- Raid results;
- Complaints and statements of citizens;
- Materials about offenses;
- Juvenile crimes.
4. INDICATORS OF THE NEGATIVE INFLUENCE OF A UNPROFESSIVE FAMILY ON THE CHILD.
BEHAVIORAL BEHAVIOR - 50%
- Vagrancy;
- Aggressiveness;
- Hooliganism;
- Theft;
- Extortion;
- Offenses;
- Immoral forms of behavior;
- Inadequate reactions to comments from adults.
CHILD DEVELOPMENT DISTURBANCES - 70%.
- Low academic performance;
- Neurasthenia;
- Lack of personal hygiene skills;
- Mental imbalance;
- Teenage alcoholism;
- Teenage prostitution;
- Diseases;
- Malnutrition;
- Study avoidance.
COMMUNICATION DISTURBANCES - 40%
- Conflicts with teachers;
- Frequent use of informal vocabulary;
- fussiness or hyperactivity;
- Conflicts with parents;
- Contacts with criminogenic groups.
5. EFFECTIVE MEASURES OF IMPACT ON A UNSUCCESSFUL FAMILY.
- Compulsory treatment for alcoholism;
- deprivation parental rights;
- Consulting;
- Educational consultations for parents;
- Help public organizations;
- Influence through the media;
- Propaganda healthy lifestyle life;
- Propaganda family values;
- Rendering financial assistance;
- Administrative fines;
- Creation of interest clubs;
- Permanent patronage;
- Providing free meals to children from disadvantaged families;
- Free treatment of children and rehabilitation during the holidays;
- Interaction of all services in early detection and individual approach to solving the problems of each family.
WHAT IS A DIFFERENT FAMILY?
We mean trouble towards the child. To talk about a child in a dysfunctional family means to talk about:
* What are the children with their own psychological and psychopathological characteristics, prone to overreaction to family troubles.
* How does family trouble affect a child who is prone to an aggravated response to all sorts of unfavorable facts.
* How a child can disturb the peace of the family, causes irritation, anger, impatience in parents to turn the family into a dysfunctional one, and the latter, in turn, can further aggravate the mental state of the child
* What should teachers do, at least in general terms, to help the child, because it is not his fault that he lives in dysfunctional family conditions.
CORRECTION OF EDUCATION IN UNSUCCESSFUL FAMILIES AND WORK WITH THESE FAMILIES.
Having studied the specifics of the life and upbringing of a child in a family, they are forced to adjust family upbringing, adjust the relationship “parents - children”, “parents - school”. In the mode of this task, we distinguish two aspects
1. Correction of education in individual families.
2. Working with dysfunctional families.
RECEPTIONS (METHODS) OF CORRECTIONAL WORK WITH UNSUCCESSFUL FAMILIES.
1. BELIEF - explanation and proof of the correctness and bias of a certain behavior or the inadmissibility of an act;
2. MORAL SUPPORT. - in relation to children from dysfunctional families, where the child feels superfluous, unnecessary;
3. INVOLVEMENT IN INTERESTING ACTIVITIES - assignment of a case that will lead to success, strengthen faith in one's own strengths:
4. WILLINGNESS TO EMPOWER - this is often absent in dysfunctional families;
5. MORAL EXERCISE for the formation of moral qualities.
DIFFERENT OPTIONS.
one. . A one-child family can also form a spoiled child with uncontrollably growing needs and, ultimately, the impossibility of satisfying them and conflicting relations with society; and a lonely person with an inferiority complex, vulnerable, insecure, unlucky and spoiled by parental love, who wants to break out of this guardianship as soon as possible.
2. A family with many children can create not only friendly children - collectivists, but also children who are pedagogically neglected, with asocial and even antisocial behavior, if
parents are busy constantly earning a livelihood, and the life and upbringing of children are not organized, left to chance.
3. A family with a low financial situation below the poverty line. For various reasons: unemployment, low wages, alcoholism, inability to build a family budget. It can please different consequences: depriving children of the necessary in satisfying material and spiritual needs. Slow down the development of children, the exploitation of children as earners of material wealth. Involvement in trade, inappropriate for age and preparedness in labor activity, undermining physical strength. Corrupting spiritually associated with a risk to life, separation from studies and systematic education at school and family. Allowing, and sometimes encouraging, immoral and illegal activities that bring income to the family.
4. An incomplete family due to a lack of material or paternal influence can give rise to a mask of feminization of boys and girls.
5. A family with free children can give rise to unpleasant, even hostile relations between children among themselves and with others.
b. A family with broken relationships, increased conflict between family members. Moreover, conflict and drama in some families increase as the child grows up, reaching maximum limits in the older adolescence and younger adolescence. The consequence may be withdrawal from the beneficial influence of family and school.
7. A family intentionally or unintentionally allowing neglect of children who find themselves outside the home and school in the companies of peers, in informal youth associations.
8. Families with child abuse occurring in different reasons: nervousness of parents due to the disastrous financial situation of unemployment, deviations in the psyche, the highest degree of dissatisfaction with their children, despotism of the father or stepfather due to unfulfilled excessive demands on them, fatigue and depression of parents. In all cases, the cruelty of parents gives rise to the cruelty of children, their coexistence with peers and teachers.
A large number of options for families where parents are not actually involved in raising children, providing them with material conditions of existence. If you do not make timely adjustments to the educational impact through the efforts of the school, then you have to deal with dysfunctional families.
WHAT DO YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT A DISABLED FAMILY?
one . Material and living conditions.
2. Emotional and moral climate.
3, The daily routine of the child in the family.
4. Methods and techniques for influencing adults on children
5. Family leisure.
6. Level of pedagogical culture of parents.
DIRECTIONS AND FORMS OF WORK WITH A UNPROFITABLE FAMILY.
| № | Areas of work with a dysfunctional family | Forms of work with a dysfunctional family. |
| 1 | Diagnosis of family dysfunction. |
|
| 2 | Individual assistance to a dysfunctional family. |
|
| 3 | Group work with parents from dysfunctional families. |
|
| 4 | Prevention of family trouble. |
|
| 5 | Community support for disadvantaged families. |
|
After making sure that the child lives in difficult conditions, the teacher must:
- Explain to parents that because of their conflicts with each other, the child suffers, that the child should not be a bargaining chip in the complex game of competing adults, but
not cooperating with each other. - If it is not possible to reason with parents who create a psycho-traumatic environment for their child that can disfigure his soul, you need to isolate the child from such parents sometime, place him in a boarding school, in a sanatorium, advise him to transfer many options to other relatives for a while, and in each specific case the best of them will be purely individual.
- If a student has already developed mental anomalies, on the basis of family conversations, he should be consulted by a child psychiatrist who comes to school for preventive examinations. And then he decides what to do.
Defects in upbringing are the first, most important indicator of a dysfunctional family; neither material, nor everyday, nor prestigious indicators characterize the degree of well-being or trouble in the family, only the relationship to the child.
Everyone is well aware of the consequences of living and growing up in a dysfunctional family.
- child neglect and homelessness.
- run away from home.
- sexual promiscuity.
- offenses and criminal activity.
- alcoholism.
Drug addiction and substance abuse.
The work with such children should be differentiated. For the convenience of this work, three groups of families can be distinguished:
Families with an irresponsible attitude to raising children, where the situation is complicated by the immoral behavior and lifestyle of parents.
Families with a low pedagogical culture of parents, where mistakes are made in the choice of means, methods and forms of work with children, where parents cannot establish the correct style and tone of relationships with children.
Families in which neglected children are allowed for various reasons, discord in the family, parents being busy with personal experiences, long business trips, parents being busy with work or social activities.
A TEACHER'S CONVERSATION WITH THE PARENTS OF A CHILD FROM A DISTRIBUTED FAMILY.
one . What good can I say about a teenager? (for the purpose of psychological location of parents, attracting them to allies.)
2. What worries me about him? (the same thing that is the subject of calling parents to school, coming to their home, discussing at a parent meeting.)
3. What, in our general opinion, are the reasons for this negative phenomenon, fact? (this causes frankness, which means it will reveal the true reasons)
4. What measures should be taken by the school as well? (development of a common strategy and tactics of education and re-education)
5. What general requirements, the general principles of transition to a child should be followed in order for the measures to be effective? (in this situation, parents frankly take the side of the teacher and actively help him.)
The task of the entire teaching staff working with adolescents. Brought up in adverse environmental conditions, which they themselves are not yet able to change. To form the internal stability of the individual, a critical perception of negative factors.
SYSTEM OF PRINCIPLES OF FAMILY EDUCATION.
- Children should grow up and be brought up in an atmosphere of goodwill, love and happiness.
- Parents must understand and accept their child as he is, and contribute to development.
- Educational influences should be built taking into account age, gender, and individual characteristics.
- The diagnostic unity of sincere, deep respect for the individual and high demands on it should be the basis of the system of family education.
- The personality of the parents themselves is an ideal model for children to imitate.
- Education should be based on the positive in a growing person.
- All activities organized in the family for the development of the child should be built on the game.
- Optimism and major are the basis of the style and tone of communication with children in the family.
REMINDER TO THE SOCIAL TEACHER ON WORKING WITH UNSUCCESSFUL FAMILIES.
- Never undertake educational actions in a bad mood.
- Clearly define for yourself what you want from the family, find out what the family thinks about this, try to convince them that your goals are, first of all, their goals.
- Do not take everything upon yourself, give the family independence, it is not necessary to control and evaluate their every step.
- Do not give final ready-made recipes and recommendations. Do not teach parents, but show possible ways overcoming difficulties, sort out right and wrong decisions leading to the goal.
- The social educator is obliged to encourage success, to notice even slight growth
and achievements of family actions. - If there are errors, incorrect actions, point them out. Rate and do
pause for the family to process what they have heard. - Let the family know that you sympathize with her, believe in her, good opinion about her, not
despite the mistakes of the parents. - A social educator is obliged to form in himself internal stability, a positive perception of facts. Such a stable position allows a person not to adapt to circumstances, but to take them into account and change them in accordance with
moral standards life. - Do not show that you have come and the family to re-educate the parents. act
in the logic of the system of "perspective lines" - from the distant perspective to the middle one and from it to the present one. - The social educator must be firm, but kind and sympathetic. Neither absolute firmness, no matter what, nor the same boundless kindness are suitable as the only fundamental principle education. All is well in due time. One must be able to apply different methods in accordance with the specific situation.
Among clearly dysfunctional families large group make up marriage unions with violation of communication. Their personal relationships are characterized by a lack of mutual respect and understanding, an increase in emotional alienation and a predominance of conflict interaction.
Naturally, the conflict family does not become immediately, but some time after the formation marriage union. It is necessary to distinguish between such concepts as "family conflicts" and "conflict families", since the conflict in the family does not mean that the family is in conflict. A conflict family is considered when spouses, even for petty reasons, start quarrels with mutual insults and abuse.
Conflict families can be both noisy, scandalous, and quiet, where marital relations are distinguished by complete alienation, the desire to avoid any interaction. Hidden tension, a hostile environment in the family - for children is no less an evil than open scandals of spouses.
The threads of family conflicts stretch very far. Their consequences are reflected not only in the state of the child's soul, but also in the whole later life. Emotional instability family relations leads to the formation of a child's feelings of fear, isolation and unsociableness. Gradually, the feeling of fear can be replaced by aggressiveness. Aggression is a protective reaction of the child's psyche. Sometimes a child is not only a witness to a conflict, but also an object of emotional discharge of those in conflict. Children from such families leave with a deep personal conflict, get an unsuccessful start in life. The child for the first time learns the roles of husband and wife, father and mother, man and woman in the process of communication with parents, he enters the world of human relations. Negative childhood memories are very harmful, they determine the thinking, feelings and actions in adulthood. Therefore, it is very important to be able to find the best options for resolving family difficulties that have arisen, not to involve children in them.
The most acceptable way out of the conflict is a compromise, an open search for the most convenient and fair solution for both sides. It is important to learn how to manage negative emotions, to be able to resolve conflict from a position of kindness. The well-known Czech psychotherapist S. Kratochvil proposed a kind of marital tactic, following which helps to prevent possible conflicts. In particular, he recommends the use of positive forms of behavior.
1. Be interested in a partner, get to know him not only positive traits but also to understand its weaknesses.
2. Listen to your partner. The ability to listen provides good contact in the family, more valuable than the ability to speak.
3. Do not abuse criticism. Criticism should not hurt the dignity of the partner, it should contain positive elements.
4. Understand your mistakes. If you understand your mistakes, then quarrels and conflicts can be avoided.
5. Enter the position of another. If a person tries to put himself in the place of another, he will try to understand the situation and avoid conflict.
6. Smile. A friendly smile is the opposite of conflict. The friendliness and goodwill of one causes a similar response in the other, relieves stress.
American psychologist Jan Gottlieb offers a number of tips to help avoid quarrels. Quarrel in private, without children, articulate the problem clearly, control emotions, put forward positive proposals.
Like 1 Bad 0
